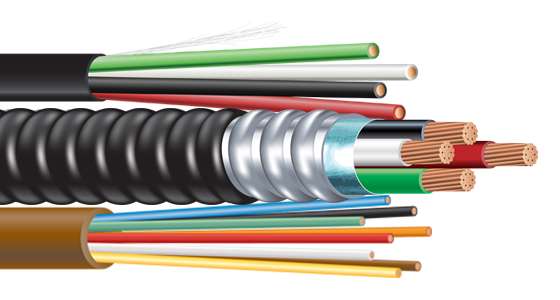
Automotive Primary Wire are a key component of the vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for delivering electrical energy from power sources (such as batteries) to various electrical and electronic devices, and are also used for signal transmission. The design and manufacture of Automotive Primary Wire must take into account the complex environment inside the car, including vibration, temperature changes, chemicals, and electromagnetic interference. The following is a detailed explanation of Automotive Primary Wire:
25mm²~1200mm² Automotive Primary Wire Grounding cable classification
Automotive Primary Wire are mainly divided into two categories:
Low-voltage wires: used for the connection of most vehicle electrical appliances, such as lighting, heating, and air conditioning systems. These wires usually work in a low-voltage system of 12V or 24V.
High-voltage wires: used for ignition systems, motors, battery management systems, and high-voltage electrical systems in modern electric vehicles/hybrid vehicles. These wires need to withstand higher voltages (such as 48V, 100V, 400V and above) and have thicker insulation and shielding layers to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Features
Material: The core of Automotive Primary Wire is copper. Usually, multi-strand copper wires (soft wires) are used instead of single-strand hard wires, which can improve the flexibility and resistance of the wires to breakage.
Insulation layer: The outside of the wires is covered with insulating materials, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), TPE (thermoplastic elastomer), etc. These materials provide protection against heat, oil, water and wear.
Color coding: The color of the wires is used to distinguish different circuits and functions, simplifying the installation and maintenance process. Two-color wires are a combination of primary and secondary colors, used for more complex or specific circuits.
25mm²~1200mm² Automotive Primary Wire Grounding cable selection and installation
Cross-sectional area: The thickness (cross-sectional area) of the wire determines its current carrying capacity and voltage drop. A larger cross-sectional area can carry more current and reduce voltage loss, but it also increases weight and cost.
Mechanical strength: The wires must have a certain mechanical strength to withstand vibration and friction during the driving of the car.
Voltage drop: To ensure that electrical equipment works properly, the wire length and cross-sectional area must be calculated to ensure that the voltage drop does not exceed a certain threshold (for example, no more than 0.5V in a 12V system).
25mm²~1200mm² Automotive Wire Ground Cable Standards and Certifications
Automotive Primary Wire follow a series of international and national standards, such as ISO, SAE, DIN, etc., to ensure quality and safety. These standards cover requirements in terms of material specifications, electrical properties, environmental testing, and durability.
25mm²~1200mm² Automotive Wire Ground Cable Applications
Automotive Primary Wire are widely used in various systems in vehicles, including but not limited to:
Starting system: connecting the starter and battery.
Lighting system: interior lighting, lights, and signal lights.
Entertainment system: audio, navigation, and communication equipment.
Safety system: airbags, ABS, ESP, etc.
Power system: engine control unit, sensors, actuators.
Comfort system: air conditioning, seat heating, window motors.
25mm²~1200mm² Automotive Primary Wire Ground Cable Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Automotive wire maintenance includes regular inspections of wires for wear, corrosion or breakage, and connectors for looseness. When troubleshooting, using a multimeter to measure resistance, voltage and current can help locate open circuits, short circuits or grounding problems.
Automotive Primary Wire are the cornerstone of ensuring the normal operation of the automotive electrical system, and their quality and reliability directly affect the overall performance of the vehicle and the safety of passengers.
XLPE, or Cross-Linked Polyethylene, is a chemically modified polyethylene material that forms a three-dimensional network structure through a cross-linking process, giving the material better thermal stability and mechanical properties. XLPE is used as an insulating material in Automotive Primary Wire because it has the following significant advantages:
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE Cable Advantages
Heat resistance: XLPE has high heat resistance and can operate at higher temperatures without softening or degrading like ordinary polyethylene. This makes XLPE wires suitable for high-temperature areas such as the engine compartment of a car.
Electrical properties: XLPE has low dielectric loss and high dielectric strength, which means it can effectively reduce signal loss and improve the insulation performance of wires.
Mechanical strength: The cross-linked structure improves the tensile strength and wear resistance of the material, making XLPE wires more durable in the automotive environment and resistant to vibration and wear.
Chemical resistance: XLPE has good resistance to a variety of chemicals and is not easily corroded by chemicals such as oils, acids, and alkalis, which is very important for the complex environment inside the car.
Flame retardancy: Although basic XLPE itself is not necessarily flame retardant, flame retardants are usually added in automotive applications to improve its fire resistance and meet the safety standards of the automotive industry.
Environmental protection: XLPE wires generally comply with environmental standards such as ROHS (Directive on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and REACH (Regulation on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals), and do not contain harmful substances such as lead, cadmium, mercury, and hexavalent chromium.
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable manufacturing process
The manufacturing of XLPE wires usually involves a special cross-linking process, which can be completed in several ways:
Chemical cross-linking: Use peroxide or other chemical initiators to promote cross-linking between polyethylene molecules at high temperatures.
Radiation cross-linking: Use electron beams or gamma rays to irradiate polyethylene to initiate a cross-linking reaction.
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable Automotive wire application
In the automotive industry, XLPE wires are widely used in:
Engine compartment: Connect ignition system, sensors, actuators, etc.
In the cab: audio system, dashboard, air conditioning system, etc.
Body: door control system, lighting system, wiper system, etc.
Electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles: battery management system, motor control, charging system, etc.
Due to its superior performance, XLPE wires occupy an important position in Automotive Primary Wire, especially in applications that require high-performance insulation and durability. As the automotive industry develops towards electrification and intelligence, the demand for high-performance wires is also increasing. XLPE wires have become an important choice under this trend due to their unique advantages.
XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) is widely used in the automotive industry as an insulation material for Automotive Primary Wire due to its excellent electrical properties and heat resistance. The following is detailed information about the structure, standards, and technical development trends of XLPE in Automotive Primary Wire:
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable structure
The basic structure of XLPE wires includes:
Conductor: Usually copper wire, which can be single-strand or multi-strand twisted soft copper wire to increase flexibility and durability.
Insulation layer: The XLPE insulation layer is a key part of the wire. It is a mesh structure formed by cross-linking polyethylene, which enhances the thermal stability and mechanical strength of the material.
Shielding layer (optional): In some applications, such as high-voltage wires or wires that need to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), there may be a layer of shielding material such as braided copper wire or metal foil.
Sheath layer (optional): In some cases, there will be an additional sheath on the outside of the wire for further physical protection or fire protection.
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable standards
Automotive Primary Wire follow a series of international and national standards that specify the size, material, performance requirements, and test methods of the wires. Standards related to XLPE include:
ISO 6722: A standard published by the International Organization for Standardization that specifies the classification and characteristics of Automotive Primary Wire.
SAE J1128: A standard developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers, USA, covering the insulation materials, dimensions and performance of Automotive Primary Wire.
DIN 72549: A standard published by the German Institute for Standardization that details the technical requirements for Automotive Primary Wire.
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable technology development trends
Lightweight: As automakers pursue lighter vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, wire materials and designs are moving towards lighter weight while maintaining or improving electrical performance.
High temperature resistance: As the degree of electrification of vehicles increases, the temperature in the engine compartment is also rising, and it is necessary to develop wire materials that can withstand higher temperatures.
Environmentally friendly materials: Concerns about environmental protection have prompted the industry to turn to recyclable or bio-based insulation materials while keeping the material’s performance unchanged.
Smart wires: Future Automotive Primary Wire may integrate sensors and smart monitoring functions to monitor the status of wires in real time, predict maintenance needs, and reduce failures.
Electromagnetic compatibility: With the increase of electronic devices in vehicles, wire design needs to better solve the problem of electromagnetic interference to ensure the stability and safety of electronic systems.
High-voltage wires: With the development of electric and hybrid vehicles, higher voltage wires are needed, which require more effective insulation and better heat dissipation.
In short, the XLPE insulation technology of Automotive Primary Wire is constantly developing to meet the new challenges of automotive electrification and intelligence, while taking into account performance, safety and environmental sustainability.
XLPE type cable is also called cross-linked polyethylene sheathed cable. Generally, domestic ones start with YJV as the abbreviation of polyethylene cable. XLPE is the abbreviation of the English name of cross-linked polyethylene. Polyethylene is a linear molecular structure that is extremely easy to deform at high temperatures. The cross-linking polyethylene process turns it into a mesh structure. This structure has strong resistance to deformation even at high temperatures. Therefore, XLPE cable is also called polyethylene cross-linked cable, which can be produced according to standards or customized according to customer requirements.
YJY means cross-linked polyethylene insulated polyethylene sheathed power cable, which can be used as underground deep buried cable and grounding cable. It is laid in automobiles, rail transit, ships, aviation, indoors, tunnels and pipelines, and can also be buried deep in loose soil, but it cannot withstand tension and pressure. YJ means that the insulation is XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene). XLPE is cross-linked PE (polyethylene) by physical or chemical methods. XLPE can greatly improve its breakdown and heat resistance, and maintain the original advantages of PE. The last Y means that the sheath is PE (polyethylene).
YJY–cross-linked polyethylene insulation polyethylene sheathed power cableYJV–cross-linked polyethylene insulation polyvinyl chloride sheathed power cable YJY has better water resistance and low temperature resistance than YJV, and YJV has better flame retardancy than YJY.
TST cables customizes 25mm²~1200mm² automotive cables, grounding cables, deep buried cables, cross-linked cables technical parameters
TST cables cross-linked cables are available in: YJV cable/ YJY cable/ YJV22 cable/ YJV23 cable/ YJV32 cable/ YJV33 cable/ YJV42 cable/ YJV43 cable.
Aluminum core name: YJLV YJLY YJLV22 YJLV23 YJLV32 YJLV33 YJLV42 YJLV43.
Cross-linked cables are available in voltage levels: 0.6/1kV, 1.8/3kV, 3.6/6kV, 6/6kV(6/10kV), 8.7/10kV(8.7/15kV), 12/20kV, 18/20kV(18/30kV), 21/35kV, 26/35kV. Commonly used are low voltage 0.6/1kV, medium voltage 6/6kV (6/10kV), 8.7/10kV (8.7/15kV), 26/35kV.
Number of cores: single core, two cores, three cores, four cores, five cores.
From the conductor cross section of the cable: 25mm², 35mm², 50mm², 70mm², 95mm², 120mm², 150mm², 185mm², 240mm², 300mm², 400mm², 500mm², 630mm², 800mm², 1000mm², 1200mm² (other sizes can be customized according to needs).
25mm²~1200mm² XLPE cable application scope:
This product is suitable for power distribution lines with rated voltage of 3.6/kV-26/35kV for power distribution.
Usage characteristics:
The rated power frequency voltage Uo/U is 3.6/6KV-26/35KV.
The maximum long-term operating temperature of the cable conductor is 90℃.
The maximum temperature of the cable conductor does not exceed 250℃ during short circuit (maximum duration does not exceed 5s).
The ambient temperature should not be lower than 0℃ when the cable is laid.
Cable bending radius: three-core cable is not less than 15 times the outer diameter of the cable; single-core cable is not less than 20 times the outer diameter of the cable.
Therefore, TST CABLES recommends that you consider specific application requirements and environmental conditions when selecting automotive cables, grounding cables, deep buried cables, and cross-linked cables. If you are ready to order YJY cross-linked cable (XLPE cable), TST cables engineers are ready to help you! You are welcome to send emails or call for quotes and free samples.
Also available in:
English