
High Pression under water
EN45545-2
- Customized Design Production
Small MOQ
Short Lead Time
- Long Time Guarantee
- Home
- /
- Waterproof Cable Submersible Cable...
Watertight Cable/Waterproof Cable/Submersible Cable Introduction
Watertight cable is mainly used for electrical connection between equipment and is required to work in underwater environment. Watertight cable is a cable with waterproof performance, which can be used in humid and flooded environments. It usually adopts special design and materials to prevent moisture from penetrating into the cable, thereby protecting the performance and safety of the cable.

Development History of Watertight Cable/Waterproof Cable/Submersible Cable
With the rapid development of shipbuilding industry and underwater ships, there are not only transverse watertight requirements for marine cables, but also longitudinal watertight requirements. At the same time, in order to obtain weak underwater acoustic signals in the interference of the ocean, the cable must have good low-noise performance. Watertight low-noise cables will make important contributions to the development of submarine cables and underwater acoustics.
There are many varieties of longitudinal watertight cables, including plastic insulated telephone soap cables filled with plaster, watertight cables filled with powder, watertight cables with watertight wall structures, etc. In the early 1960s, the United Kingdom began to trial-produce filled cables. Since 1967, all the wiring cables of the British Post and Telecommunications General Administration have adopted filled cables. In the late 1960s, the United States began to produce filled cables in two major departments, Bell Laboratories and Essex Company, and expanded their application in direct buried cables. By 1977-1978, filled cables accounted for 100% of direct buried cables. Some other capitalist countries, such as Japan and West Germany, also attached great importance to the development of watertight relays.
Structure of watertight cable/waterproof cable/submersible cable
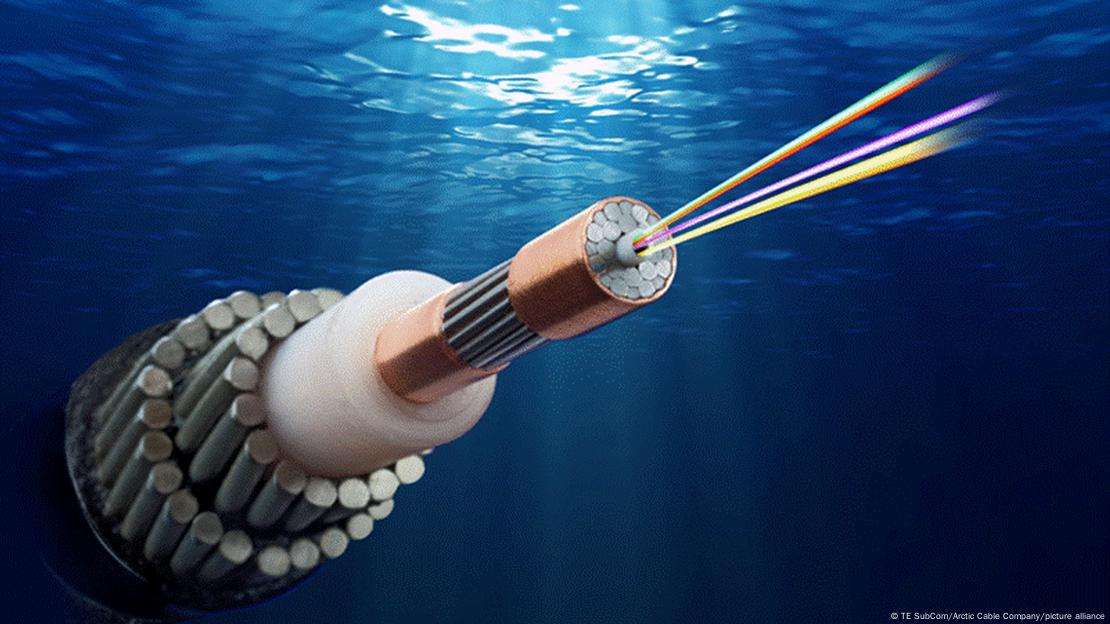
In China, there are also some varieties of longitudinal watertight cables. Our company has developed 900# —2 irradiated polyethylene high-strength radio frequency cables and polyethylene fully filled longitudinal sealed cables. Brother units also have cables filled with petroleum jelly. These cables focus on solving the longitudinal leakage and moisture-proof problems of cables.
Conductor: multi-strand fine twisted bending-resistant ultra-fine oxygen-free copper wire/tinned copper wire, in line with mainstream international standards such as IEC60228, EN, UL, etc.
Insulation: PE, PUR, TPE and other materials
Wire core: black numbers and white numbers, more than 3 cores with yellow-green grounding wire (yellow-green optional)
Structure: anti-twist layering, or grouped twisted pairs + multiple twisted gap filling
Inner sheath: modified low-viscosity strong extrusion inner sheath (optional)
Inside: video screen line, communication line, etc. can be added according to customer needs
Shielding: tinned copper mesh braided shielding, density > 80%
Sheath material: polyether polyurethane/ordinary polyurethane material, etc.
Sheath color: black/gray/orange/yellow, can also be customized.
The reason why watertight cables can maintain their electrical performance and mechanical integrity in humid or underwater environments is mainly due to their special material selection and structural design. The following are the key materials that make up watertight cables and their respective functions:
Outer sheath materials of watertight cables/waterproof cables/submersible cables Polyvinyl chloride (PVC):
PVC is a common outer sheath material that is widely used because of its relatively low price, good wear resistance and weather resistance. However, for applications that require higher waterproof performance, PVC may not be the best choice.
Polyurethane (PU)cable:
Polyurethane outer sheath has better wear resistance and oil resistance, and is suitable for occasions that require higher mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE)cable:
XLPE is a polyethylene material obtained by chemical cross-linking treatment, which has higher heat resistance and electrical insulation performance and is suitable for applications in high temperature and high pressure environments.
Insulation layer materials of watertight cables
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR)cable:
TPR is a material with good elasticity and flexibility, suitable for making the insulation layer of cables, and can provide good electrical isolation effect.
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer (TPU)cable: Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer (TPU) can be divided into polyester type and polyether type according to molecular structure, and can be divided into injection molding grade, extrusion grade, blow molding grade, etc. according to processing method.
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE):
TPE has excellent aging resistance and softness, and is suitable as an insulation material for watertight cables, especially in applications that require frequent bending.
Fluoroplastic (such as FEP, PTFE):
Fluoroplastic is an ideal material for making high-performance watertight cable insulation due to its excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance and non-water absorption, especially for applications in extreme environments.
Watertight cable/Waterproof Cable waterproof layer material
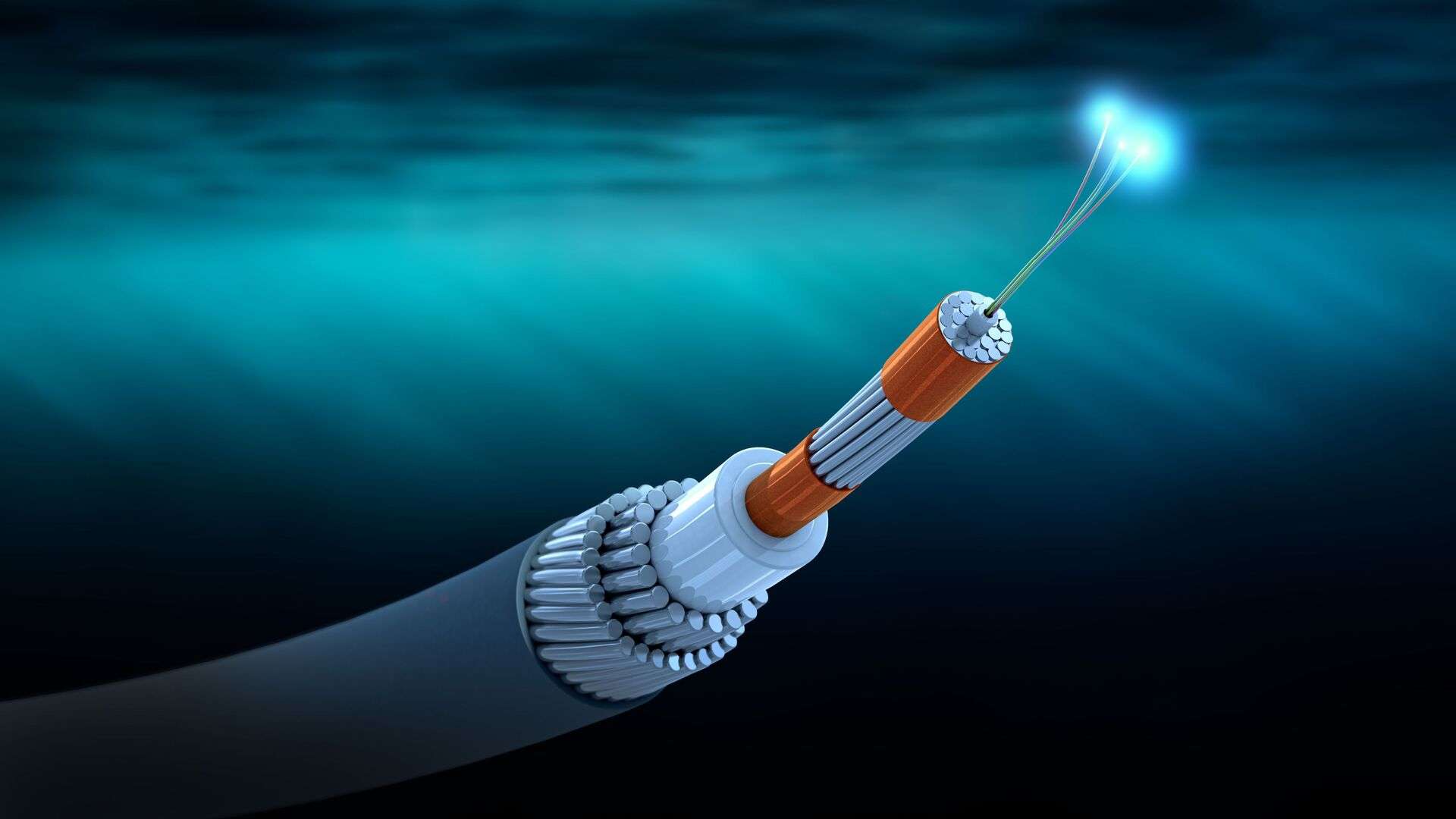
Waterproof tape:
Inside the cable, a layer of waterproof tape is usually wrapped around the conductor to prevent moisture from penetrating into the cable.
Waterproof filler:
Some cables fill the gaps with waterproof glue or grease to further improve the waterproof effect.
Waterproof coating:
A layer of waterproof coating is applied to the surface of the cable to effectively prevent moisture from intruding.
Watertight cable shielding layer material
Metal braid:
Using a metal braid as a shielding layer can not only improve the cable’s anti-interference ability, but also enhance its mechanical strength.
Aluminum foil or copper foil:
In some cases, a layer of aluminum foil or copper foil is added to the insulation layer as a shielding layer to improve electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) performance.
Watertight cable reinforcement layer materials
Steel wire armor:
For applications that require additional mechanical protection, such as submarine cables, steel wire armor is used to enhance the tensile strength and compressive resistance of the cable.
Fiber reinforced materials:
Fiber reinforced materials (such as aramid fibers) can also be used to improve the mechanical strength of the cable when metal armor is not required.
Watertight cable joints and terminal materials
Waterproof sealant:
Waterproof sealant is used at the joints and terminals of the cable to ensure the sealing of these parts and prevent moisture from entering.
Waterproof sealing ring:
Where the cable passes through the wall or equipment housing, a waterproof sealing ring is used to close any possible gaps.
Through the reasonable combination and design of these materials, watertight cables can provide reliable electrical connections in various harsh environments to ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
Classification of watertight cables/waterproof cables/submersible cables

Watertight cables are divided into longitudinal watertight and transverse watertight.
Key points of transverse watertightness: It is mainly to fill the gaps between multi-core cables with glue and water-blocking tape.
Key points of longitudinal watertightness: In addition to filling the gaps between cables, the conductor twisting must also be filled with glue.
Currently, commonly used longitudinal watertight cables can be divided into six categories according to their uses and characteristics, namely:
Longitudinal watertight power cables;
Longitudinal watertight coaxial cables;
Longitudinal watertight signal cables (double-grain structure);
Longitudinal watertight control cables;
Longitudinal watertight optical cables;
Longitudinal watertight composite cables (including optical fiber, signal, power line and control line or any combination thereof, this type of electricity fee is lower.
Features of watertight cables/waterproof cables/submersible cables
- Waterproof performance: Watertight cables use special waterproof design and materials to effectively prevent moisture from penetrating into the cable. This waterproof performance can provide reliable power, signal and data transmission in humid and flooded environments.
- Sealing performance: Watertight cables usually have good sealing performance, which can prevent moisture from entering the cable through the cable sheath or connector. This sealing performance can ensure the long-term reliable operation of the cable in underwater or humid environments.
- Durability: Watertight cables usually have good durability and can resist the influence of environmental conditions such as moisture, flooding, corrosion, etc. They usually adopt water-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials and structures to ensure long-term stable performance.
- Wide range of applications: Watertight cables are suitable for various scenarios that require waterproof performance, such as underwater equipment, outdoor equipment, ships, marine engineering, mines, etc. They can transmit power, signals and data to meet the needs of different applications.
Advantages of watertight cables/Waterproof Cable
- Small outer diameter, light weight, small space occupation (a series of problems that can usually be solved with multiple cables can be replaced by a composite cable);
- Low customer procurement cost, low construction cost, and low network construction cost;
- It has superior bending performance and good lateral pressure resistance, and is easy to construct;
- It provides multiple transmission technologies at the same time, with high adaptability and scalability of the same equipment, and the product has a wide range of applications;
- It provides huge bandwidth access;
- Save costs, use optical fiber as a reserved use to the home, and avoid secondary wiring;
- Solve the problem of equipment power consumption in network construction (avoid repeated laying of power supply lines).
Main application areas of watertight cables/waterproof cables/submersible cables :
Ocean and underwater applications
Watertight cables, due to their unique waterproof properties, are of great value in various occasions that require water resistance or work in humid environments.
Ocean exploration and research:
Underwater detectors: Equipment used for deep-sea exploration, geological surveys and other activities usually requires watertight cables to transmit power and data.
Underwater robots (ROV/AUV): Remotely controlled or autonomous underwater vehicles rely on watertight cables to power and transmit control signals when performing tasks.
Ocean engineering:
Offshore wind farms: Reliable electrical connections are required between the foundation structure and tower of offshore wind turbines, and watertight cables are an ideal choice.
Oil drilling platforms: In offshore oil and gas extraction platforms, watertight cables are used to connect various equipment to ensure their normal operation in saltwater environments.
Ships and submarines:
Shipborne equipment: The navigation system, communication equipment, engine control system, etc. on the ship require watertight cables to ensure their normal operation
when operating on the water.
Submarine cables: The connection between internal and external equipment in submarines also requires the use of watertight cables to ensure the safety of underwater operations.
Industrial Applications
Factory Automation: In some production lines that need to be cleaned regularly, watertight cables can prevent water and detergents from entering the cable interior to ensure the continuous operation of the production line.
Food Processing: In food processing plants, watertight cables are used to connect equipment that needs to be frequently flushed with water, such as conveyor belts, packaging machines, etc.
Mining: In underground mines, watertight cables are used to connect important facilities such as lighting systems, ventilation equipment, and hoists to ensure the normal operation of equipment in humid environments.
Infrastructure Construction
Urban Drainage Systems: In urban drainage systems, watertight cables are used to connect equipment such as water pumps and valve controllers to ensure the normal operation of drainage systems during rainy seasons or floods.
Bridges and Tunnels: In bridge and tunnel construction, watertight cables are used to connect lighting, ventilation, monitoring and other systems to ensure the safety of these infrastructures in humid or underwater environments.
Water Treatment Plants: In sewage treatment plants and water supply systems, watertight cables are used to connect various monitoring instruments, pump station equipment, etc. to ensure electrical safety during water quality treatment and transportation.
Agriculture and Gardening
Irrigation system: In the farm irrigation system, watertight cables are used to connect sprinkler equipment, drip irrigation systems, etc. to ensure that the cables are not affected by water during the irrigation process.
Greenhouse control: The humidity in the greenhouse is high, and watertight cables are used to connect temperature control systems, spray systems and other equipment to maintain the environmental conditions required for plant growth.
Special environment
Swimming pools and spas: In swimming pools and spas, watertight cables are used to connect lighting, filtration systems, heating equipment, etc. to ensure the safety and comfort of visitors.
Outdoor billboards: In outdoor LED displays or billboards, watertight cables are used to connect power supplies and control units to prevent rainwater intrusion and cause malfunctions.
Product recommendations and technical parameters of watertight cables/waterproof cables
Rated voltage: 300/500V; (other specifications can be customized)
Test voltage: 1500V;
Temperature range: -65℃~+125℃; (other specifications can be customized)
Minimum bending radius of seawaterproof cable during continuous movement: 4× cable outer diameter
Longitudinal and transverse pressure resistance: 10Mpa
Bending radius: 6D
Bending according to: GJB1916 standard, 10,000 times.
Watertight sheath material: TPU
19 cores (4*0.5 shielded signal + 4*2*26AWG Category 7 network cable + 2*1.0 power supply + 50 ohm coaxial + 4*0.75 control cable) (other specifications can be customized)
Scope of application of watertight cable/waterproof cable/submersible cable
Watertight cable is suitable for high watertight, resistant to bending multi-core integrated cables in the fields of ships, offshore oil platforms, deep-sea resource exploration, etc. It can also be used for various types of submersible motor lead wires, wires and cables used for telescopic/drag in deep water, submersible pumps and various underwater working electrical appliances from underwater to water power connection.
Some common standards and considerations for watertight cable ratings:
IP rating
One of the most commonly used standards is the International Ingress Protection Rating (IP rating), which is a set of protection ratings defined by the IEC 60529 standard to indicate the degree of protection of electrical products against external solid and liquid intrusion. For watertight cables, the main concern is water resistance:
IP68: This is the highest level of water resistance, indicating that the device can be immersed in water at a specified pressure and depth for a long time without water ingress. Specifically, IP68 means that the device can be fully immersed in water under conditions specified by the manufacturer (such as water depth and duration).
Water pressure test rating
In addition to the IP rating, watertight cables may also be classified according to their ability to withstand water pressure. This classification usually involves the durability of the cable under different water pressure conditions:
4.5 MPa: Some watertight cables can withstand 4.5 MPa (approximately equal to 45 bar) of longitudinal water pressure.
6.0 MPa: A higher level of watertight cables can withstand 6.0 MPa (approximately equal to 60 bar) of lateral and longitudinal water pressure.
10.0 MPa / 70.0 MPa: For applications that need to work in extremely high water pressure environments, such as deep-sea exploration equipment, watertight cables may need to withstand water pressures of up to 10.0 MPa or even 70.0 MPa.
Other performance indicators
In addition to the above-mentioned protection level and water pressure test, the performance of watertight cables can also be measured by the following indicators:
Voltage level: The maximum voltage level that the cable can withstand, such as 500V or 1000V.
AC withstand voltage test: The ability of the cable to withstand an AC voltage higher than the rated voltage for a specific time without breakdown.
Operating temperature range: The ability of the cable to work normally within a specified temperature range.
Mechanical strength: Including the tensile strength and compressive strength of the cable.
Watertight cable application cases
Depending on the above grades, watertight cables are suitable for a variety of environments:
Shallow water applications: For equipment connections in lakes and rivers, lower-grade watertight cables are usually used.
Deep-water applications: For marine exploration and deep-sea equipment, high-grade watertight cables are required to ensure that performance is maintained under high pressure.
Special environment: If the cable needs to work in extreme temperature or chemical corrosion environment, a customized watertight cable is required.
Technical development trend of watertight cable/waterproof cable/submersible cable
Currently, TST CABLES Researchers are working to develop more high-performance watertight cable materials to meet the needs of the future market. For example:
High-performance polymer watertight cable: Develop new polymer materials, such as modified polyurethane (TPU), polyimide (PI), etc., to improve the water resistance, chemical resistance and mechanical strength of the cable.
Nanomaterial watertight cable: Use nanotechnology to enhance the waterproof and mechanical properties of the cable, such as by adding nanoparticles to improve the microstructure of the material.
Bio-based material watertight cable: Explore the use of bio-based polymers to replace traditional plastic materials to reduce the impact on the environment.
Degradable material watertight cable: Develop watertight cable materials that can be naturally degraded under certain conditions to reduce the harm of waste to the environment.
Micro watertight cable: With the development of microelectronics technology, watertight cables tend to be smaller in size and are suitable for applications that require compact design.
Lightweight design watertight cable: Reduce the weight of the cable by optimizing material selection and structural design, improve portability and installation convenience.
Modular watertight cable components: Develop detachable and replaceable modular components to facilitate cable repair and upgrade and reduce maintenance costs.
Watertight cable with built-in sensors: integrated temperature, humidity, pressure and other sensors to achieve real-time monitoring of cable operation status and early warning of potential faults.
Wireless communication watertight cable: using wireless communication technology, the cable can transmit data remotely, which is convenient for remote management and maintenance.
Intelligent manufacturing watertight cable: using advanced automated production equipment to improve production efficiency and product quality and reduce production costs.
High-voltage watertight cable: developing watertight cables suitable for higher voltage levels to meet the needs of power transmission and distribution.
High-frequency transmission watertight cable: optimizing the design of the cable, improving the data transmission rate and signal integrity, suitable for high-speed communication networks.
Multifunctional composite watertight cable: integrating multiple functions such as waterproof, fireproof, and rat bite prevention to improve the comprehensive performance of the cable.
Deep-sea exploration: with the development of marine science, the application of watertight cables in deep-sea exploration, seabed observation and other aspects will be more extensive.
New energy industry: in the fields of new energy such as offshore wind power and ocean energy generation, the demand for watertight cables will continue to grow.
Extreme environment: developing watertight cables suitable for special environments such as extreme temperature and high pressure to meet the needs of special applications.
How to choose a watertight cable?
When choosing a watertight cable, users should determine the appropriate grade based on the actual application requirements. Considering the environmental conditions (such as water depth, water pressure, temperature changes, etc.) that the cable will face, as well as the expected service life, it is crucial to choose the appropriate watertight grade.
The grade of a watertight cable is mainly determined by its protection performance, including IP rating and ability to withstand water pressure. These grades help users choose the most suitable cable products according to specific application requirements, ensuring safe and reliable operation in various underwater or humid environments. If you are not sure how to choose the right watertight cable, you can communicate with TST cables senior technical engineers through email to obtain solutions and apply for free samples.
Related by TST:
Do you know the selection criteria for Mil spec wire aerospace wire?
Do you know the selection criteria for military-standard airport lighting...
Read MoreEssential Guide for Purchasing LSOH Cables in High Temperature Environments UL758
In high-temperature operating environments such as metallurgy, petrochemicals, rail transit,...
Read MoreThree Reasons Why High-End Industrial Parks Choose Overhead Cables for Cable Upgrades
Many people associate high-end industrial parks with underground cables and...
Read MoreSay Goodbye to the “Spider Web”! Low-Voltage Overhead Cables: Urban Power Grid Upgrades
Have you ever noticed the dense, spider web-like tangled exposed...
Read MoreAlso available in:
Arabic
English
German
Indonesian
Japanese
Russian
Spanish
Thai
Vietnamese
Portuguese (Brazil)









