Analysis of fire hazards and causes in the laying of wires and cables in power systems
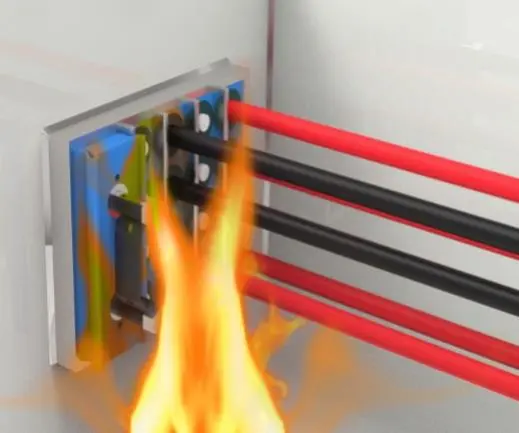

In high-rise buildings, because wires and cables are laid in bundles and erected on wire racks, once a fire occurs in wires and cables, the consequences are disastrous. Because the insulation layers used in wires and cables are flammable rubber, polyvinyl chloride and other hydrogen-rich organic compounds, the heat generated when burning is 19000~46000kJ/kg. The melting point of the copper core of wires and cables is about 1038℃, and the melting point of the aluminum core is 658℃, while the melting point of the insulation layer of wires and cables is far lower than these values, such as the melting point of polyvinyl chloride plastic is only 120℃. When the melting temperature of the hot spot of a group of bundled wires and cables reaches 800~1100℃, the threat to high-rise buildings is particularly serious. There is a lot of smoke in the accident, and it is difficult to observe the source of fire, and the accident handling is very difficult. The fire tragedies in Sichuan Department Store and Kowloon Building in Hong Kong in recent years were all caused by wires and cables.
Electrical fire accidents can also cause other chain accidents. Generally speaking, plastic wires and cables not only burn quickly, but also produce a large amount of toxic and harmful gases, such as hydrogen chloride and carbon monoxide, which put people in a state of suffocation and poisoning, and face the risk of death. At the same time, when extinguished, the halide gas will generate strong acid mist through combustion reaction, causing “secondary pollution”, which will cause modern intelligent high-rise electrical and electronic equipment to be corroded by strong acid, and the consequences are also quite serious.
Preventive measures for fire hazards in the laying of wires and cables in power systems
We must attach great importance to it ideologically, strictly control each link such as design, manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and inspection, implement full process management, and improve the safety and reliability of cables. The design and selection of wires and cables should be appropriate. Technical treatment should be carried out on wires and cables in high-rise construction. Fireproof plugging materials should be strictly used between buildings, between floors, between floors and walls, between racks and floors, between elevator shafts and racks, and in the control room, etc., and they should be sealed thoroughly, so that when wires and cables catch fire, the flames will not spread to other directions. Especially for the bundled groups of wires and cables, the direction should be indicated, and the electrical bridge boxes, settlement boxes, and joint boxes should be strictly isolated and closed to prevent the accident from expanding and spreading after the fire occurs.
Keep the cables away from heat and fire sources. When laying cables, the cable pipelines should be as far away from steam and oil pipelines as possible, and a certain safe distance should be maintained between them. Cables should not be laid in trenches for flammable gases or flammable liquids. If laid in thermal trenches, insulation protection measures should be taken for the cables, and cables should not be laid overhead in places with explosion or fire hazards.
Carry out fire prevention treatment in areas where fire is prone to occur or cause fire to spread. When laying cables, flammable and explosive materials should be isolated. In cable sections that are easily affected by the outside world, necessary fire prevention treatment should be carried out. In order to effectively prevent the spread of fire and reduce fire losses, fire walls and fire-blocking sections can be set up in cable trenches, cable tunnels and other places to control the fire in a certain cable section to reduce the scope of the fire. The cable trenches near oil-filled electrical equipment must be sealed well. The holes in the cable interlayer leading to the control room and all the wall holes in the shaft, the cable penetrations from the floor, etc. must be tightly sealed with fire-resistant materials. The fire resistance limit should not be less than 1h to prevent the cable fire from spreading to non-fire areas. Fire walls and fire-blocking sections should be set up at the junction of different factory buildings or workshops, the outdoor entry into the indoor, the busbar section of the distribution room, the junction of different voltage distribution devices, the cable connection of different units and main transformers, and every 100m of long-distance cableways; at the connection between the tunnel and the main control, centralized control, and network control room, a fire wall with a door should be set up. In case of fire, the fire door can be closed automatically or manually from a distance; in the tunnel at the factory wall, a fire door with a lock should also be set up. Automatic alarm and fire extinguishing devices should be set up. In order to effectively extinguish the initial fire of cables, automatic alarm and fire extinguishing devices can be installed at appropriate locations of cable interlayers and cable tunnels to eliminate the initial fire of cables in the bud.
In order to reduce the hidden dangers of cable fires, full attention should be paid to and effective measures should be taken in the three links of design, operation and construction. All relevant units should clarify the cable fire prevention responsibility system and regularly organize personnel to inspect and implement cable fire prevention measures. In short, as long as every effort is made to minimize the possibility of cable ignition and extended combustion, cable fire accidents will be effectively controlled.
TST CABLES measures to prevent wire and cable fires:
1. Ensure the construction quality, especially the production quality of cable heads must strictly meet the requirements.
2. Strengthen cable operation monitoring to avoid overload operation of cables.
3. Conduct cable tests on schedule and deal with abnormalities in a timely manner.
4. Keep the cable trench dry to prevent the cable from getting damp, causing insulation degradation and short circuit.
5. Clean the dust accumulated on the cable regularly to prevent the accumulated dust from spontaneous combustion and causing cable fire.
6. Strengthen the regular inspection and maintenance of cable loop switches and protection to ensure their reliable operation.
7. When laying cables, keep a sufficient distance from the heat pipe, control cables should not be less than 0.5 meters; power cables should not be less than 1 meter. Control cables and power cables should be arranged separately in slots and layers, and cannot be overlapped between layers. For parts that do not meet the regulations, cables should take flame retardant and heat insulation measures.
8. Install fire alarm devices to detect fires in time to prevent cables from catching fire.
9. Take fire retardant measures. TST CABLES cable sealing fire retardant measures include:
Wrap the cable with heat-insulating and flame-resistant materials. When the cable is on fire, the wrapped cable is isolated from the fire by the heat-insulating and flame-resistant materials to avoid burning. If the cable itself catches fire, the lack of oxygen in the wrapped body can extinguish the fire by itself, preventing the fire from spreading to the outside of the wrapped body.
The holes through which the cables pass through the walls, bottoms of trays, and shafts are tightly sealed with fire-resistant materials to prevent the high-temperature smoke from spreading and spreading when the cables catch fire, causing the fire to expand.
Apply fire-retardant paint on the cable surface.
Wrap the parts of the cable that need to be ignited with fire-resistant tape.
Set up heat-resistant fireproof boards between cable layers to prevent the cable layers from catching fire and expanding the fire.
Set up segmented partition walls and fireproof doors in the cable channel to prevent the cables from catching fire and expanding the fire.
10. Equip with necessary fire-fighting equipment and facilities. Overhead cable fires can be extinguished with commonly used fire-fighting equipment, but automatic or remote-controlled fire-fighting devices, such as 1301 fire-fighting devices, water spray fire-fighting devices, etc., should be installed in cable interlayers, shafts, trenches, tunnels, etc.
Firefighting of cable fires
When a cable fire occurs, the alarm should be called immediately, the system and direction of the burning cable should be immediately identified, the burning cable should be adjusted to operate as soon as possible, and the power supply of the burning cable should be cut off and the operation should be stopped. Cables produce toxic gases when they burn, so special attention must be paid to protection when fighting cable fires.
Also available in:
English