Thermal Classification of Insulating Materials and Applications
Insulating materials play a vital role in electrical and electronic equipment, ensuring proper operation and preventing electrical failures. The heat resistance of insulating materials is one of the most important indicators of their performance, and insulating materials of different heat resistance levels are suitable for different working environments and temperature requirements. In this article, TSTCABLES will introduce the heat-resistant classification of insulating materials in detail, and list the permissible working temperatures at all levels, as well as the common main insulating materials and cable insulation.
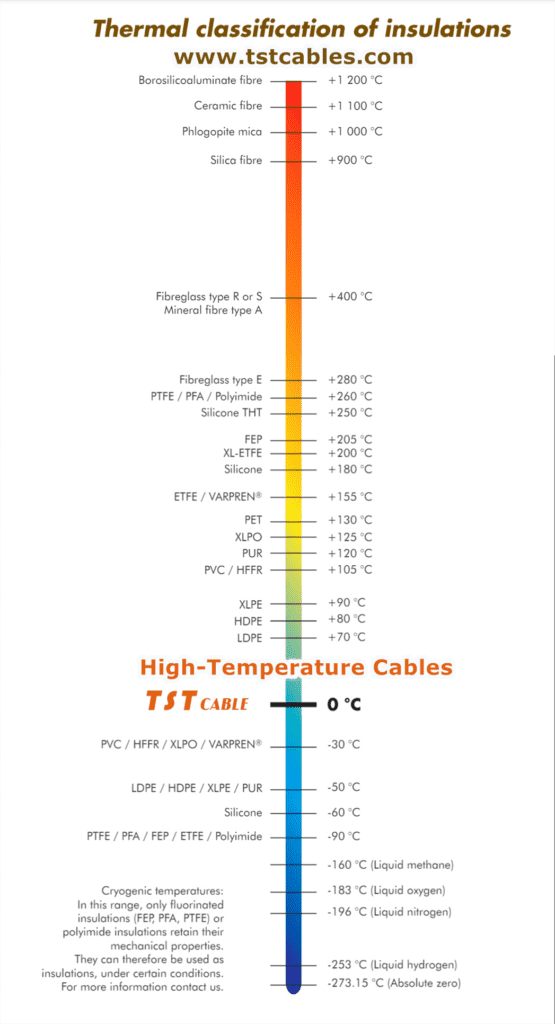
The temperature classification of high-temperature cable insulation is mainly based on its ultimate working temperature.
- Y level: the ultimate working temperature is 90℃. The main insulating materials include wood board, cotton, cardboard, textiles and so on.
- A grade: the ultimate working temperature is 105℃. For example, cotton and insulating materials for enameled wires.
- E grade: The ultimate working temperature is 120℃. Often used for high-strength enameled wire insulation materials.
- B Grade: Ultimate working temperature is 130℃. Can use mica sheet products, glass wire, etc. as insulating materials.
- F class: the ultimate working temperature is 155℃. Applicable insulating materials include glass, enameled cloth, silicone organic, etc.
- H Grade: The ultimate working temperature is 180℃. This grade does not use any organic binder and impregnant inorganic materials such as EM, quartz, etc.
- C grade: the ultimate working temperature is usually above 180℃. These cables usually do not use organic materials, but inorganic materials with higher temperature resistance.
High temperature cable insulation temperature classification
Y: 90 °C • A: 105 °C • E: 120 °C • B: 130 °C • F: 155 °C • H: 180 °C • C: > 180 °C
Application of different heat-resistant grade insulating materials
Insulation materials of different heat-resistant grades have a wide range of applications in electrical equipment and electronic products, the following are some common applications:
- Class Y and Class A: Insulation materials for use in low-temperature areas or less demanding applications, such as light bulbs, switches and other products.
- Grade E: Suitable for applications with high temperature requirements, such as motors, transformers, generators, inductors, etc.
- Grade B: Particularly suitable for insulating materials used directly in winding coils in applications such as electric motors.
- Grade F: Widely used in high temperature applications such as industrial furnaces, transformers, inductors and cables.
- Grade H: Especially suitable for high temperature occasions such as motors and generators, and can adapt to high frequency vibration.
Types of insulating materials
Organic insulating materials: including phenolic resins, epoxy resins, acrylates, etc., widely used in electronics, electrical, chemical, aerospace and other fields.
Inorganic insulating materials: including glass fiber, silicate, quartz, etc., mainly used in high-temperature industrial fields, such as glass, cement, metallurgy, ceramics and so on.
Composite class insulating materials: composite by organic and inorganic insulating materials, a wide range of applications, to meet the requirements of different areas of insulating material performance.
High temperature cable insulation material temperature
Polyvinyl chloride insulated power cables, wire core of the conductor long-term allowable operating temperature of 700 ℃
Cross-linked polyethylene insulated power cables, the maximum temperature of the conductor, the normal operation of 90 ° C
Ethylene-propylene insulated chlorosulfonated polyvinyl chloride rubber sheathed power cables, the maximum permissible conductor temperature of 90 ° C
In addition, for PVC insulated cables, according to standards such as GB/T5023, GB/T9330 and GB/T12706, the classification and working temperature of PVC insulating materials are as follows:
PVC/C, PVC/A, PVC/D: The maximum or long-term allowable working temperature of the conductor is 70℃. Among them, PVC/D is soft type.
PVC/E, J-90: the maximum working temperature of the conductor is 90℃.
TSTCABLES reminds consumers that they need to pay attention to: the actual working temperature of high-temperature cables may be affected by a variety of factors, such as the installation environment, load current, heat dissipation conditions. Therefore, when you choose cables, in addition to considering the temperature rating of the insulating material, you also need to comprehensively consider other factors to ensure the safe operation of the cable. If you have any questions or needs about high quality high temperature cable, please feel free to contact us by email.
TSTCABLES, the world’s leading manufacturer of high quality high temperature cables( -190°C to +1400°C)
TSTCABLES’s high temperature cables can easily cope with extreme high and low temperature environments with excellent cold and heat resistance. High-quality high-temperature cables for extreme conditions from -190°C to +1400°C, high-temperature challenges without fear! Since 2003, TSTCABLES‘ stringent requirements, expertise, innovation, cutting-edge technology and investment in equipment and human resources have been our mainstay, helping us to develop more efficient and stable products to meet the needs of our customers in different fields.
TSTCABLES’ high temperature cables can easily cope with extreme high and low temperature environments with excellent cold and heat resistance. The use of special insulating materials ensures that the cables still transmit power stably at high and low temperatures without error or danger. Whether for industrial production, energy transmission or other temperature operations, our high temperature cables are your most reliable choice. Resistant to high and low temperatures, without losing power, to protect your production safety and efficiency.
Also available in:
English




