1. Integrated wiring system 1.1 Horizontal subsystem, calculation method for cable usage:
Average cable length = (horizontal distance of the farthest information point + horizontal distance of the nearest information point) / 2 + 2H (H-floor height)
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Number of cables per box = cable length per box / actual average cable length
Number of cable boxes required = total number of information points / number of cables per box
Note: The horizontal distance of the farthest and nearest information points is the actual horizontal distance from the floor wiring room (IDF) to the information point, including the actual horizontal routing distance. If an IDF is set up on multiple floors, the corresponding floor height should also be included. The above “average cable length” calculation formula is suitable for the situation where a floor wiring room (IDF) is set up on the first or third floor.
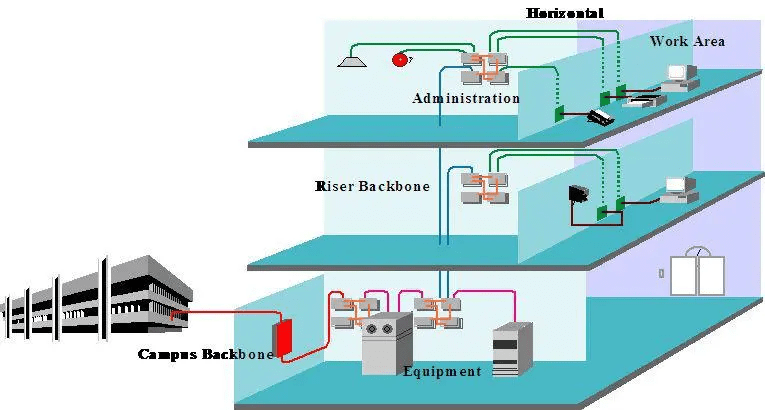
1.2 Calculation method of copper cable usage for trunk subsystem:
Average cable length = (farthest IDF distance + nearest IDF distance)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Number of cables per axis = cable length per axis/actual average cable length
Number of required axis of cable = total number of IDFs/number of cables per box
Note: The farthest and nearest IDF distances are the actual distances from the floor wiring room (IDF) to the main distribution frame (MDF) of the network center, which mainly depends on the floor height and the horizontal distance from the weak current well to the equipment room (MDF). The number of pairs of large-pair cables is calculated as 1:2 (i.e. 2 pairs of twisted pairs are configured for 1 voice point), and 25/50 pairs of cables are selected for reasonable design. 100 pairs of large-pair cables are generally not selected because they are difficult to construct.
1.3 Trunk subsystem, calculation method for optical cable usage:
Average optical cable length = (farthest IDF distance + nearest IDF distance)/2
Actual average optical cable length = average optical cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total amount of optical cable required = total number of IDF × actual average optical cable length
Note: The farthest and nearest IDF distances are the actual distances from the floor wiring room (IDF) to the main distribution frame (MDF) of the network center, which mainly depends on the floor height and the horizontal distance from the weak current well to the MDF. If the bidding documents have clear requirements for the number of optical fiber cores, single mode, and multimode, the design will be based on the requirements. The general choice is 6-core multimode optical cable. 2. Cable TV System 2.1 Star Wiring Calculation Method: This method is defined as: All floor branch distributors are concentrated in the weak current room, and an RF cable is independently laid from each user terminal (socket) to the corresponding weak current room and connected to the branch distributor. Horizontal cable (usually RG6), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (horizontal distance of the farthest user terminal + horizontal distance of the nearest user terminal) / 2 + 2H (H – floor height)
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 3)
Total number of cables required = total number of user terminals x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The horizontal distance of the farthest and nearest user terminals is the actual distance from the floor distribution box to the farthest and nearest terminal user sockets, including the actual horizontal route distance. If a floor distribution box is set up on multiple floors, the corresponding floor height should also be included. Trunk cable (usually RG11/RG9), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (distance from the farthest floor distribution box + distance from the nearest floor distribution box)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total number of cables required = total number of floor distribution rooms x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The distance from the farthest and nearest floor distribution box is the actual distance from the floor distribution box to the satellite or cable TV center room (or extension amplifier), which mainly depends on the floor height and the horizontal distance from the weak current well to the cable TV center room. 2.2 Calculation method for branch connection wiring: Branch connection wiring is usually divided into three parts: household cable, horizontal cable, and trunk (vertical) cable. A. Cable for household entry: (usually RG6 specification), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (distance to the farthest user terminal + distance to the nearest user terminal)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 3)
Total number of cables required = total number of user terminals x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The distance to the farthest and nearest user terminals is the actual distance from the splitter to the nearest terminal user socket and the farthest user terminal. B. Horizontal branch cables (usually RG11), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (farthest branch/terminal resistor distance + nearest branch/terminal resistor distance)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total number of cables required = total number of horizontal cables x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The farthest and nearest branch distances are the actual distances from the distributor box between the floor distribution rooms to the farthest and nearest branch, including the actual horizontal routing distance. If multiple floors share a floor distributor, the corresponding floor height should also be included. C. Trunk cable (usually RG12 or RG11), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (distance from the farthest floor distribution box + distance from the nearest floor distribution box)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total number of cables required = total number of floor distribution boxes x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The distance from the farthest and nearest floor distribution boxes is the actual distance from the floor distribution box to the satellite or cable TV room, which mainly depends on the floor height and the horizontal distance from the weak current well to the satellite or cable TV room. 3. Security system 3.1 Video surveillance system 3.1.1 The calculation method of network camera network cable is basically the same as that of the integrated wiring system 3.1.2 Power cable calculation method: RVV2*1.0 specification.
Method 1: Since the distribution of cameras is relatively scattered (especially in groups of buildings). Therefore, it is recommended to calculate according to 1/2~1/3 of the length of the video cable.
Method 2: Lay one power cable for every 8 cameras: Total number of power cables required = (total number of cameras/8) * actual average cable length in video cable calculation.
3.2 Burglar alarm system 3.2.1 Calculation method for two-core alarm cables: RVV2*0.5 specification.
Average cable length = (distance to the farthest alarm front-end device + distance to the nearest alarm front-end device)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total number of cables required = total number of front alarm devices x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The farthest and nearest alarm front-end distances refer to the actual distances from the security center machine room (or alarm keyboard, expansion module) or to the farthest and nearest alarm front-end devices from the machine room (or alarm keyboard, expansion module), (pay attention to the floor height). When the length and width of the group building are significantly different from the length and width of the main building, it is required to calculate the actual average cable length separately. The calculation method for the four-core alarm cable is the same as above. RVV4*0.5 Specifications 3.2.2 Calculation method for alarm network bus: Since most alarm network buses are one (or one) bus, and a few are two (or more) buses, it is required to calculate according to the actual bus route. Total number of cables required = actual bus route length × 1.1 + termination tolerance (m) Note: Termination tolerance = the number of devices (usually alarm keyboards, expansion modules) that need to be connected to the bus * 6 IV. Background music and emergency broadcast system 4.1 Calculation method for horizontal cables: Horizontal part cables (usually ZR-RVS 2*1.0):
Average cable length = (longest horizontal distance + shortest horizontal distance) / 2 + H (H—floor height)
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (speaker termination tolerance)
Total number of cables required = total number of horizontal cables (i.e. number of broadcast partitions) x actual average cable length (m)
Note 1: The longest and shortest floor horizontal distances are the actual distances from the weak current room to the longest floor and the shortest floor. Note 2: If two speaker loops are required on one floor (i.e. one broadcast zone), such as the hotel guest rooms (or office rooms in an office building) and the public corridor need to be divided into two loops, the above-mentioned “average cable length” should be calculated separately, and then the “actual average cable length” should be calculated. It should be noted that the “total number of horizontal cables (i.e. the number of broadcast zones)” needs to be “doubled” at this time. Note 3: Loudspeaker termination tolerance = number of loudspeakers on the measured horizontal distance floor * (9 for guest rooms or offices, 6 for corridors); 4.2 Trunk cable calculation method: Broadcast trunk cable (usually ZR-RVS 4*1.0), cable usage calculation method:
Average cable length = (distance of the farthest floor distribution box + distance of the nearest floor distribution box)/2
Actual average cable length = average cable length × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 6)
Total number of cables required = total number of floor distribution boxes x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The distance of the farthest and nearest floor distribution boxes (broadcast partitions) is the actual distance from the floor distribution box to the broadcast center room, which mainly depends on the floor height and the horizontal distance from the weak current well to the broadcast center room. 5. Multimedia digital conference and sound reinforcement system Since this system has a wide variety of equipment and many types of connecting wires, but the number (length) is not long, it is recommended to quote the cable calculation method of this system in the form of auxiliary materials and calculate it at 1.5-2% of the total price of the system equipment. The special connection cable for digital conference system should be quoted separately, and the calculated quantity is the actual distance from the digital conference control host to the chairman machine or representative machine * 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 3). 6. Calculation method of various cables from the monitoring point to the DDC box of the building equipment monitoring system: usually there are RVV2*1.0, RVS2*1.0, BVS2*2.5, RVVP2*1.0, RVV8*1.0 (for DDC box to equipment distribution box) and other specifications.
Average cable length = (distance from the farthest monitoring point + distance from the nearest monitoring point)/2 +H (H-floor height)
Actual average cable length = average cable length × total number of DDC monitoring points × 1.1 + (termination tolerance, usually 3)
Total number of cables required = total number of monitoring points x actual average cable length (meters)
Note: The distance from the farthest and nearest monitoring points is the actual distance from the DDC box to the monitoring point or monitoring equipment. Various types of cables should be calculated separately. If the DDC box is installed in the controlled equipment room, such as the cold and heat source room, air conditioning unit, fresh air unit and other equipment rooms, the “actual average cable length” in the cold and heat source room can be calculated as 15 meters (but pay attention to the DDC installation position of the monitoring cooling tower); the “actual average cable length” in the air conditioning unit, fresh air unit and other equipment rooms can be calculated as 10 meters.
Also available in:
English